
TOPOGRAPHY, SOIL HORIZONS, AND EROSION/DEPOSITION
This document illustrates the methods and tools integrated with
GRASS GIS
which support spatial analysis of relationship between soil
properties, topography and erosion processes in 3D space and time.
The study area is located at experimental farm near Munchen, Germany.
Detailed survey was performed in this area resulting in approx.
2000 points with elevation data and 400 points with soil core data.
Point data were transformed to 2D raster maps using
using regularized spline with tension
implemented in GRASS as s.surf.tps.
The following images and movies show the spatial distribution of data and
selected raster maps representing terrain and soil horizons,
visualized in 3D space as combination of multiple surfaces, color,
cutting panes, transparency and points.
Flow related topographic parameters needed for hillslope erosion
modeling are computed by flow tracing program
r.flow, the combined grid-vector
flowtracing algorithm used in this program
is described in Mitasova and Hofierka 1993
and Mitasova, Mitas et al. 1995).
As an option, r.flow can be used to simulate the temporal
changes in spatial distribution
of waterflow. The following movies show different ways how the results
of such simulation can be visualized using programs
xganim
and SG3d.
Sediment transport capacity is computed as a function of waterflux and slope,
(see Mitasova, Hofierka et al. 1995)
the next movie shows it as a surface draped over elevation surface.
 Sediment transport capacity (movie - 65Kb)
Sediment transport capacity (movie - 65Kb)
Topographic potential of landscape for erosion/deposition is computed
a change in sediment transport capacity
(see Mitasova, Hofierka et al. 1995).
Comparison of results of erosion/deposition model with the depth
of colluvial deposits illustrates the capability of erosion deposition
model to predict location of major deposition areas.
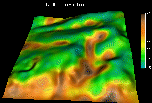
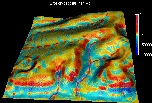
Using Nviz
it is possible to explore 3D spatial relations
between terrain shape, results of erosion/deposition model
and thickness of colluvial deposits
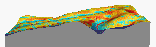
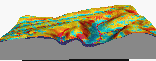
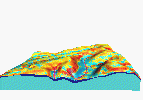 Slicing through colluvial deposits (movie - 68,164 bytes)
Slicing through colluvial deposits (movie - 68,164 bytes)
Data used in this document were provided by Prof. K. Auerswald
from Technical University Munchen, Germany, in cooperation with Steven Warren
from USA CERL.
Images and animations for this document were created using the
GRASS4.1 program SG3d and
GRASS4.2 program Nviz.
Programming, computations and visualization
for this project was done by
Environmental modeling and visualization group
at U.S.Army CERL (H. Mitasova, W. Brown, M. Astley, T. Baker, I. Kosinovsky),
interpolation methods were designed by
Lubos Mitas at NCSA, flowtracing program was developed by Jaro
Hofierka, Maros Zlocha from Comenius University, Bratislava,
Slovakia,
and Joshua Caplan from
University of Illinois.
This work was partially supported by DOD Strategic Environmental Research
and Development Program. (
SERDP).

 GMSL Modeling & Visualization
GMSL Modeling & Visualization
Home Page
 Sediment transport capacity (movie - 65Kb)
Sediment transport capacity (movie - 65Kb)
 Sediment transport capacity (movie - 65Kb)
Sediment transport capacity (movie - 65Kb)

 Slicing through colluvial deposits (movie - 68,164 bytes)
Slicing through colluvial deposits (movie - 68,164 bytes)
 GMSL Modeling & Visualization
GMSL Modeling & Visualization