1. Enable Spatial Analyst
Under View... Toolbars select Spatial Analyst
|
|
2. Calculate Slope and Aspect
From the Spatial Analyst toolbar, select Surface
Analysis... Slope
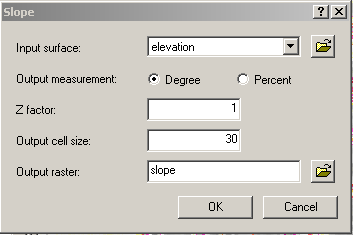
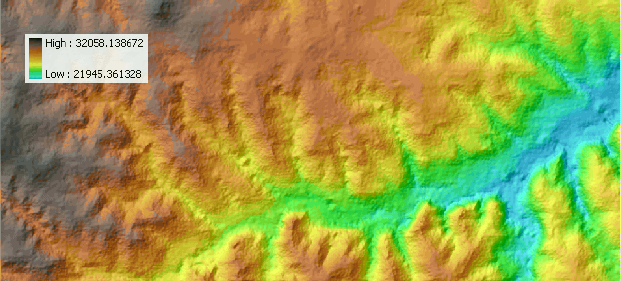
Enter the elevation layer, select Degree, and enter
output information.
|
 |
| Give the new theme
name slope |
 |
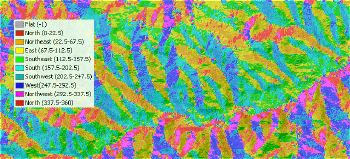
From the Spatial
Analyst toolbar, select Surface Analysis... Aspect
Give the new theme name aspect
|
 |
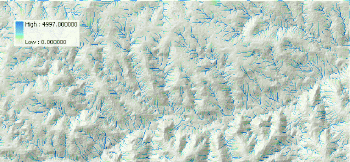
3. Raster Calculator
From the Spatial Analyst toolbar, select Raster Calculator
Build an expression:
FlowAccumulation(FlowDirection([elevation]))
Evaluate
Make the new theme permanent and change the name to flowacc
|
 |
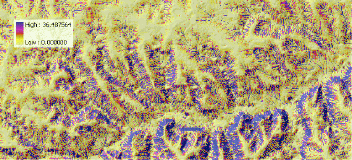
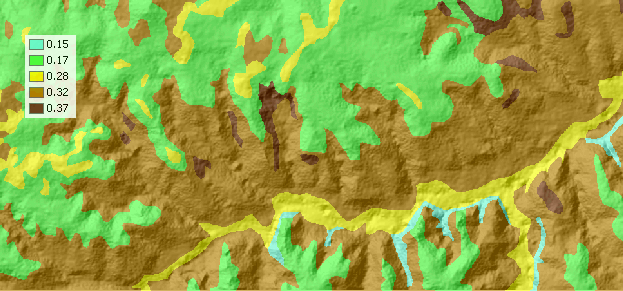
Build an expression in the Raster Calculator
Note: to get contributing area per unit width we multiply by cell area and divide by resolution
leading to mult. by resolution below. The width unit [m] cancels out in steps 4-6 by computing
the directional derivative leading to final erdep rate per cell in ton/acre.year, for 10m cell
divide by 4046 to get ton/year eroded from a grid cell
(!!! skip conversion to radians - multiplication by 0.01745 - in ArcGIS9.2 in all expressions below):
(for prevailing rill erosion):
Pow([flowacc] * resolution , 1.6) * Pow(Sin([slope]
* 0.01745) , 1.3)
Evaluate
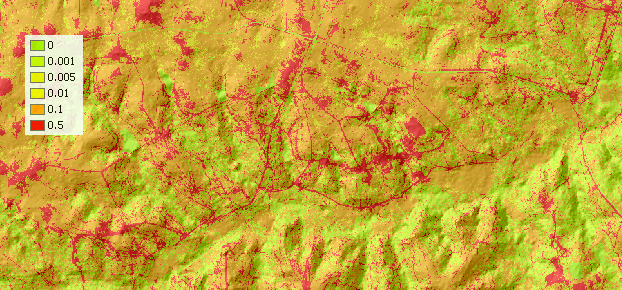
Make the new theme permanent and change the name to sflowtopo
|
 |
(for prevailing
sheet erosion):
[flowacc] * resolution * Sin([slope] * 0.01745)
Evaluate
Make the new theme permanent and change the name to sflowtopo
|
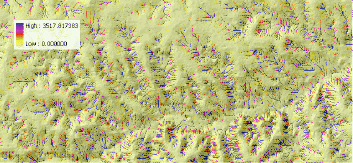 |
Build an expression in the
Raster Calculator:
note: R changed from the original 280 to R=120 (Oct 28, 2008)
[sflowtopo] * [kfac] * [cfac] * 120 * Cos((([aspect]
* (-1)) + 450) * .01745)
Evaluate
Make the new theme permanent and change the name to qsx
|
|
Build an expression in the
Raster Calculator:
[sflowtopo] * [kfac] * [cfac] * 120 * Sin((([aspect]
* (-1)) + 450) * .01745)
Evaluate
Make the new theme permanent and change the name to qsy
|
|
4. Select qsx in the Spatial
Analysis Toolbar
Select Surface Analysis... Slope
Give the new theme name qsx_slope
Select Surface Analysis... Aspect
Give the new theme name qsx_aspect
|
|
5. Select qsy in the Spatial
Analysis Toolbar
Select Surface Analysis... Slope
Give the new theme name qsy_slope
Select Surface Analysis... Aspect
Give the new theme name qsy_aspect
|
|
6. Raster Calculator
Build an expression
Cos((([qsx_aspect] * (-1)) + 450) * .01745) * Tan([qsx_slope]
* .01745)
Give the new theme name qsx_dx
Build an expression
Sin((([qsy_aspect] * (-1)) + 450) * .01745) * Tan([qsy_slope]
* .01745)
Give the new theme name qsy_dy
Build an expression
[qsx_dx] + [qsy_dy] for prevailing rill erosion
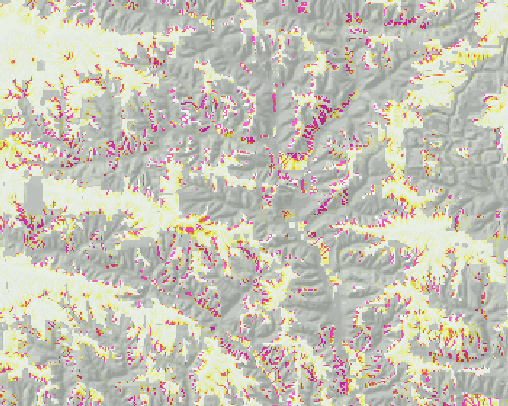
Give the new theme name erdep
|
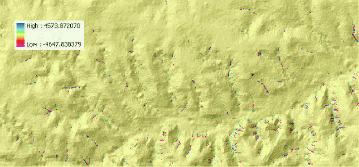 |
([qsx_dx] + [qsy_dy]) *
10. for prevailing sheet erosion
Give the new theme name erdep |
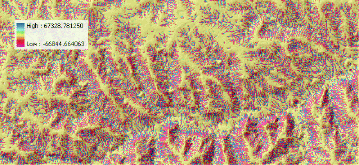 |
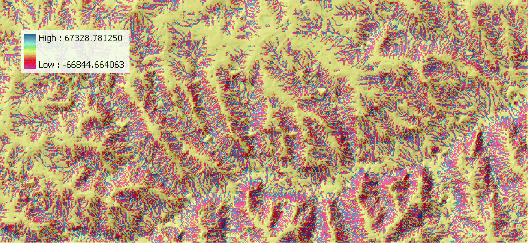








![]() HOME
H. Mitasova, et al., Geographic
Modeling Systems Lab, UIUC
HOME
H. Mitasova, et al., Geographic
Modeling Systems Lab, UIUC